Table of Contents
1 Current project situation
2 Hub and Spoke network
3 VNet Peering
4 Lab
4.1 Lab Topology
4.2 Lab VNet
4.2.1 Lab VNet Peering
4.3 Lab Functions
4.3.1 Lab Functions - VNet
4.3.2 Functions - Access Restrictions
4.4 Lab API Management
4.4.1 Lab API Management - VNet
4.5 Lab Data Flow and Requests
4.5.1 VM Cloud to On-Premise-Function
4.5.2 VM On-Premise to On-Premise-Function
4.5.3 VM Cloud to Cloud-Function
4.5.4 VM On-Premise to Cloud-Function
5 Code and Deployment
6 Further information
1 Current project situation
Our current project contains about 20 Azure Functions Apps in Premium Plan. These Functions Apps are connected with an Express Route to the On-Premise network and use a VNET subnet which is part of the On-Premise network.
This setup has a few drawbacks:
- Based on the permissions, network changes can only be done by the company network group and not by the project group.
- Because it's the same network, subnets and IP addresses are limited
- Azure Function Apps running in a Premium Plan can scale out to 100 instances. Which means up to 100 IPs will be required for running the Azure Function Apps.
2 Hub and Spoke network
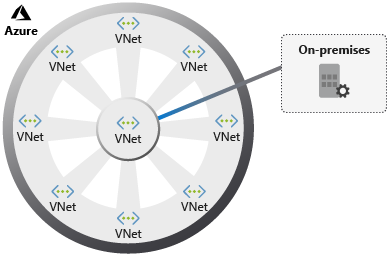 Implement a hub-spoke network topology on Azure
Implement a hub-spoke network topology on Azure
The hub is a virtual network in Azure that acts as a central point of connectivity to your on-premises network. The spokes are virtual networks that peer with the hub, and can be used to isolate workloads. Traffic flows between the on-premises datacenter and the hub through an ExpressRoute or VPN gateway connection.
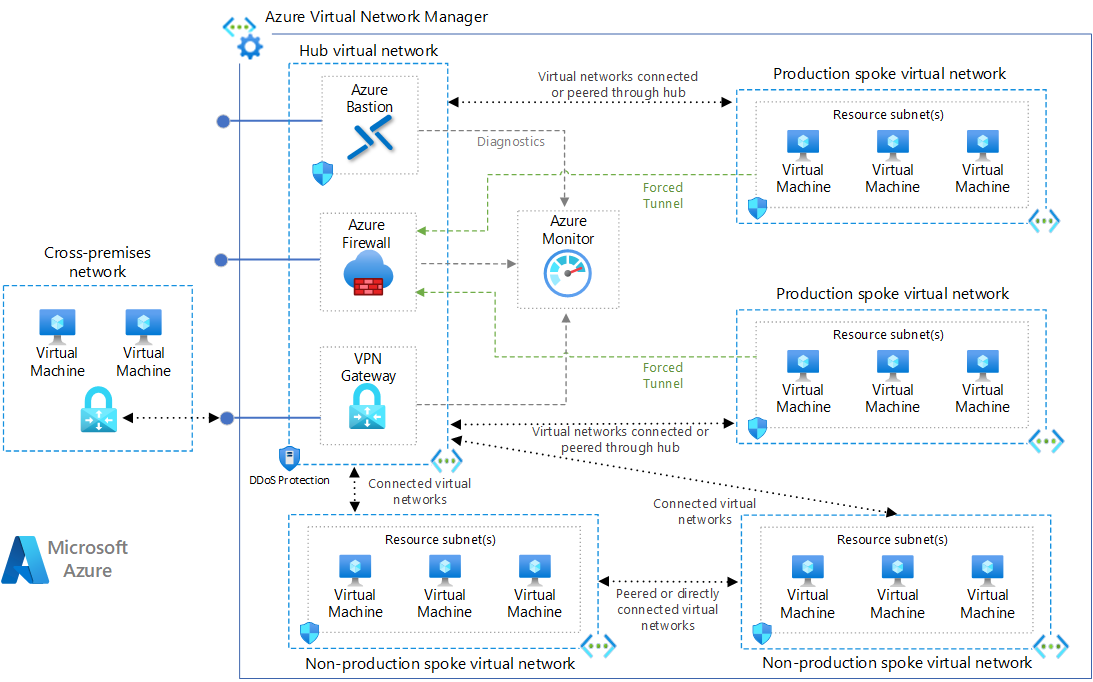 Hub-spoke network topology in Azure
Hub-spoke network topology in Azure
3 VNet Peering
With VNet Peering, Azure Virtual Networks can be connected:
Azure supports the following types of peering:
- Virtual network peering: Connect virtual networks within the same Azure region.
- Global virtual network peering: Connecting virtual networks across Azure regions.
4 Lab
For evaluation purpose, a lab has to be created with the following resources:
- Azure Function Apps
- Azure API Management
- VNets
- VMs
- for connection testing
All resources are deployed in the same region.
The lab simulates a Hub and Spoke network. HTTP-Requests are made from VMs to test the data flow.
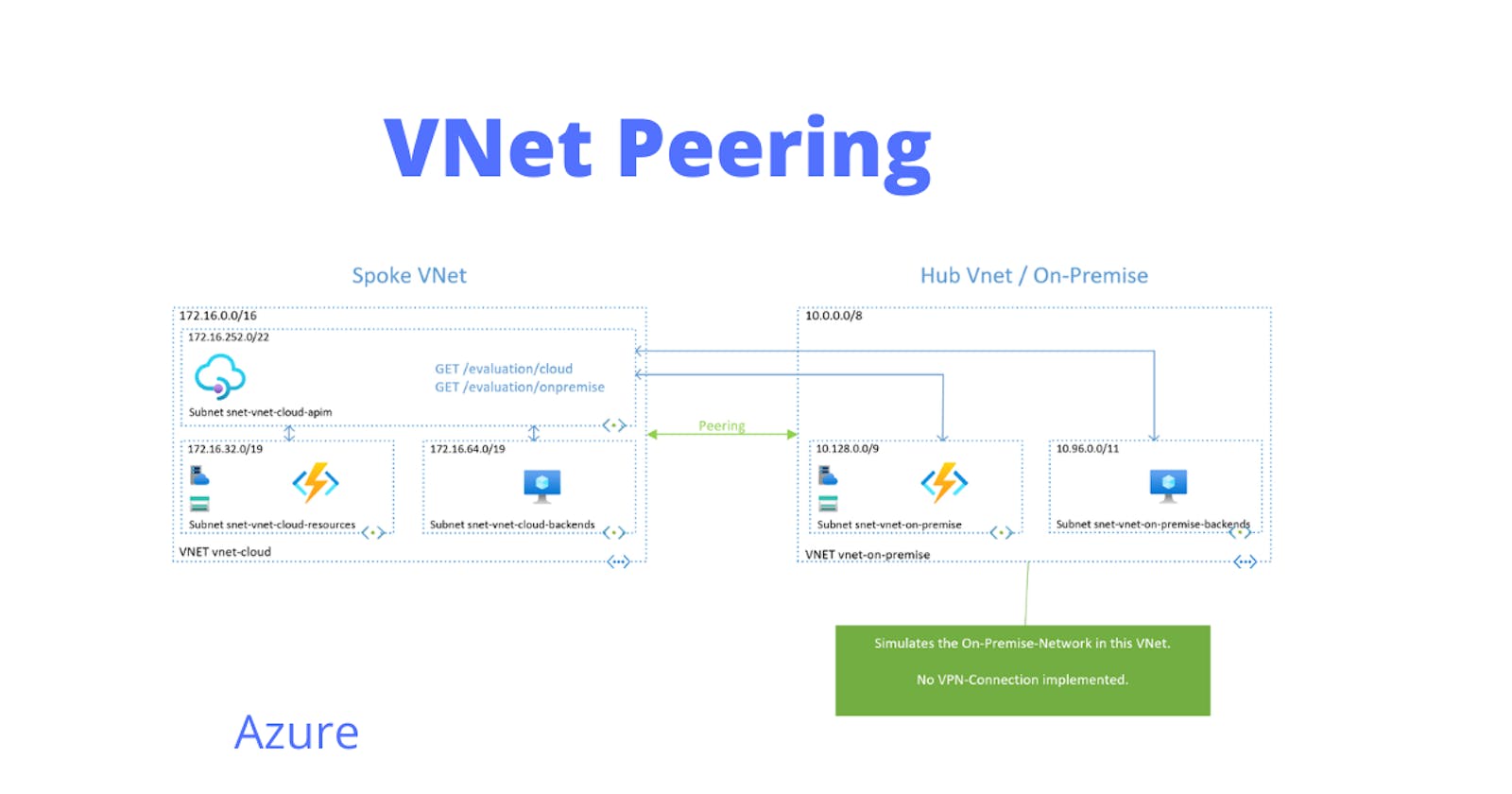
4.1 Lab Topology
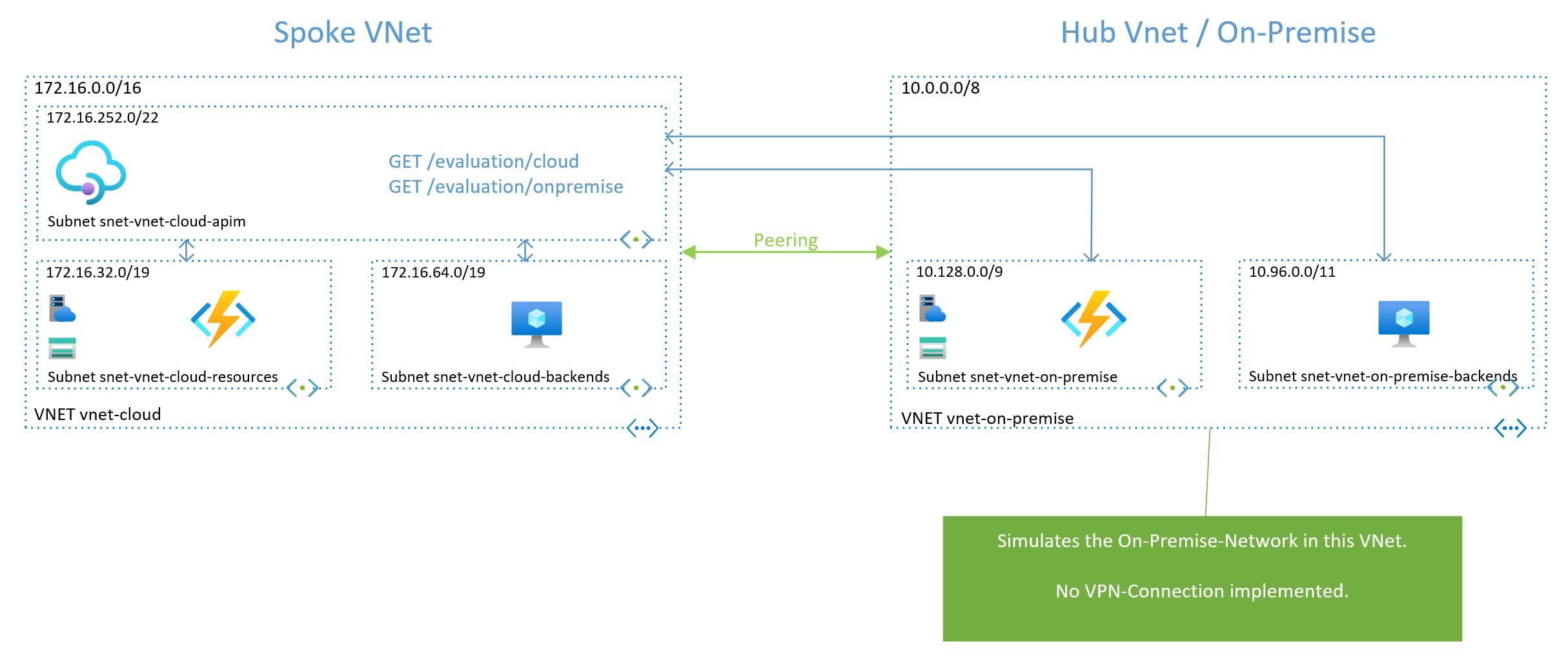
The lab consists of two VNets:
- vnet-cloud
- 172.16.0.0/16
- Spoke
- vnet-on-premise
- 10.0.0.0/8
- Hub and simulates the On-Premise-Network
- simpler setup
API Management provides HTTP-Endpoints which forwards the requests to the Functions.
4.2 Lab VNet
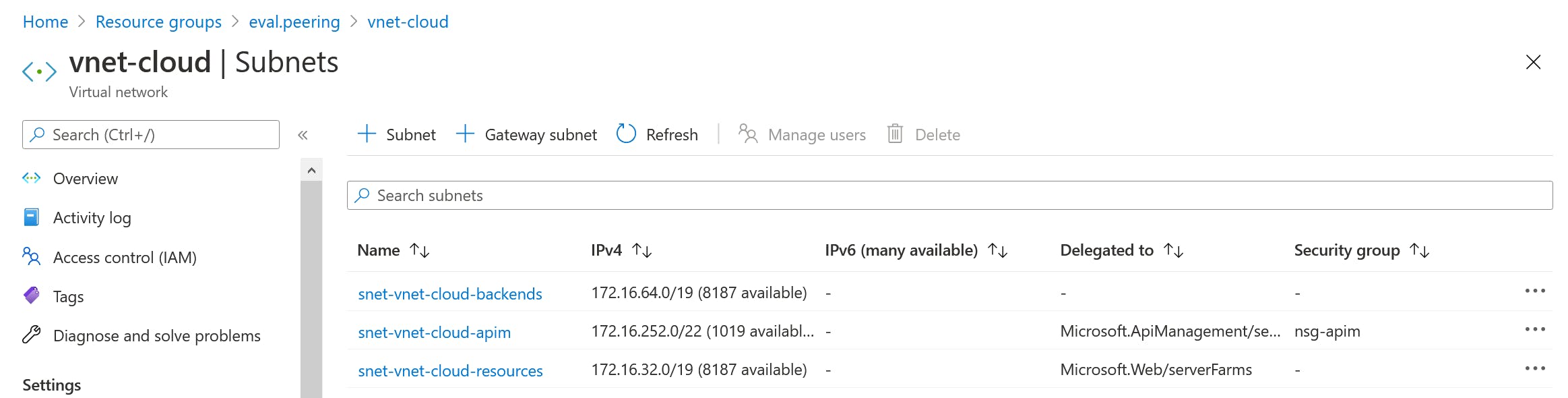
vnet-cloud with three subnets:
- snet-vnet-cloud-backends
- 172.16.64.0/19
- for VM for making Http-requests
- snet-vnet-cloud-apim
- 172.16.252.0/22
- for API Management
- snet-vnet-cloud-resources
- 172.16.32.0/19
- for Azure Function App
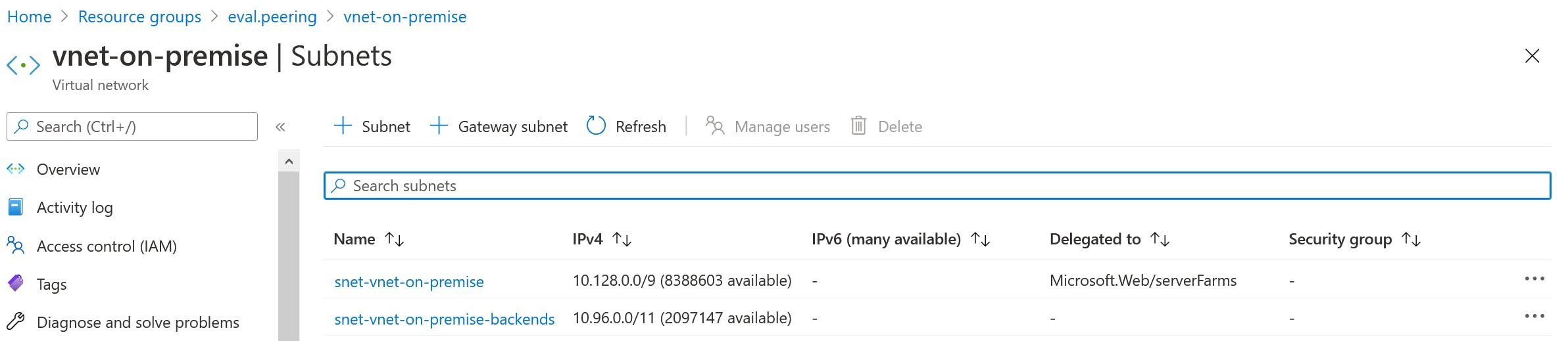
vnet-on-premise with two subnets:
- snet-vnet-on-premise-backends
- 10.96.0.0/11
- for VM for making Http-requests
- snet-vnet-on-premise
- 10.128.0.0/9
- for Azure Function App which represents a on-premise system
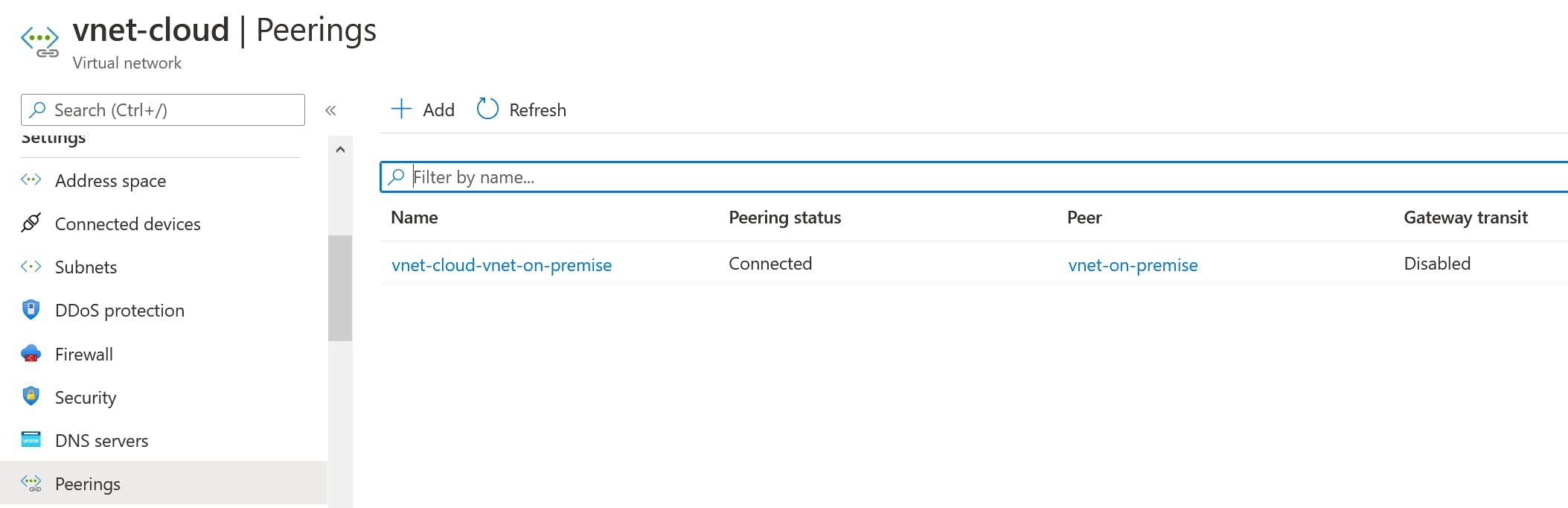
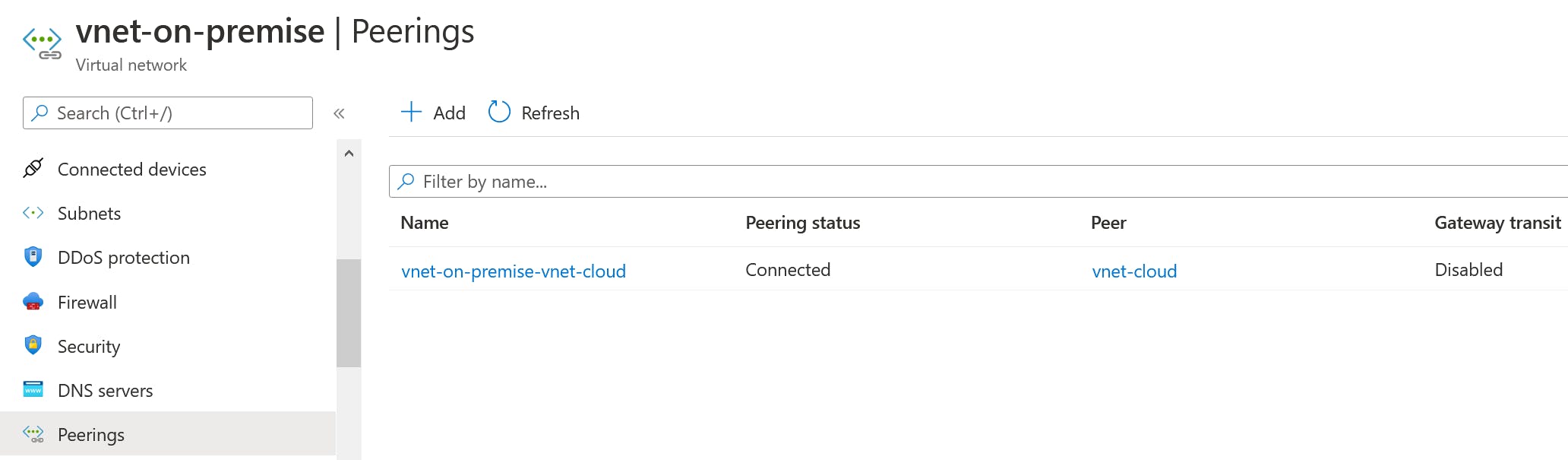
4.2.1 Lab VNet Peering
Both VNet Peerings are created with an ARM Template in the same subscription. Please check the How-To Guide if you want to create VNet Peering in different Subscriptions or with different deployment models.
4.3 Lab Functions
Azure Functions networking options
VNet Integration depends on use of a dedicated subnet. When you provision a subnet, the Azure subnet loses 5 IPs for from the start.
Two Azure Functions Apps with HttpTrigger are deployed in the different VNets:
- https://func-cloud.azurewebsites.net/api/cloudtrigger
- https://func-on-premise.azurewebsites.net/api/onpremisetrigger
Function func-on-premise in VNET vnet-on-premise simualtes a On-Premise-System with Http-Endpoint.
4.3.1 Lab Functions - VNet
At least the Azure Function Premium Plan has to be used to configure Functions Apps with VNet integration.
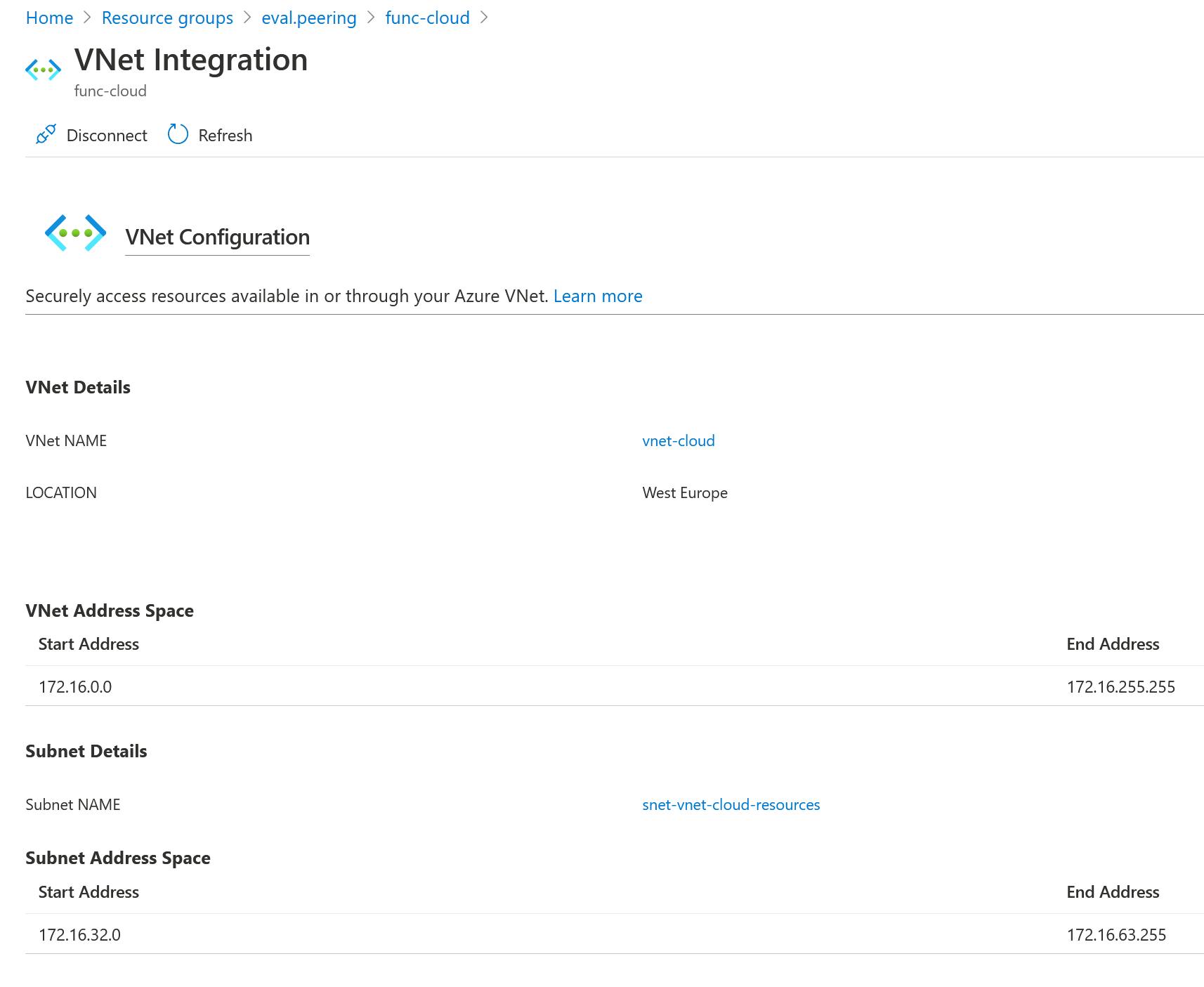
The storage accounts are also part of the (VNet)[docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/comm..:
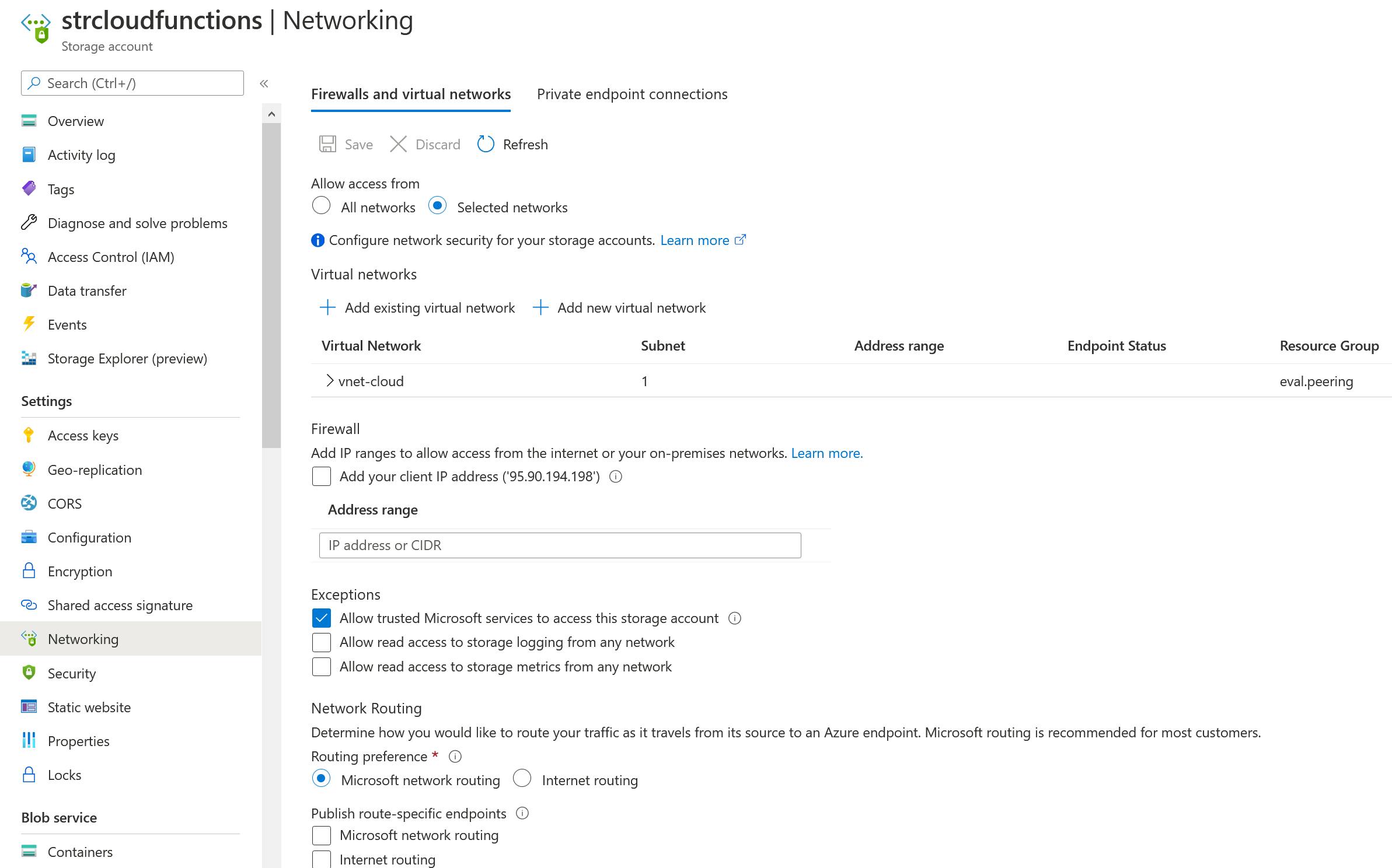
4.3.2 Functions - Access Restrictions
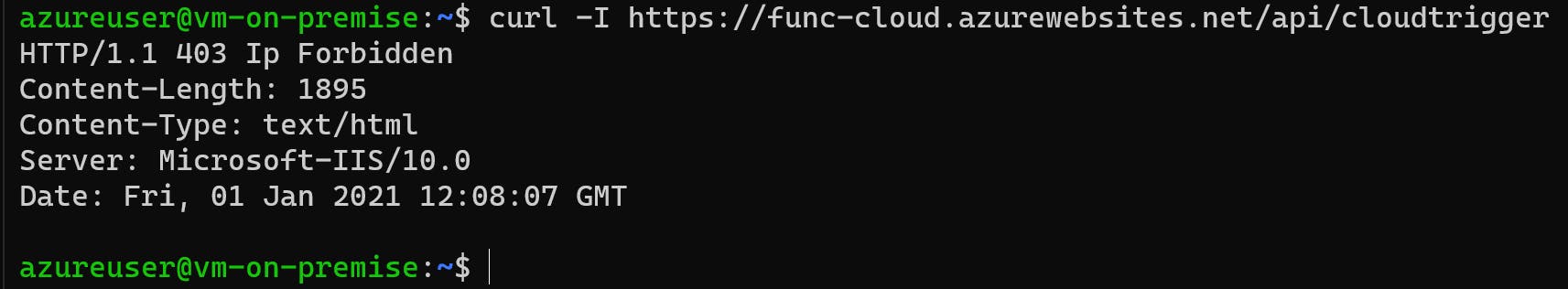
Following Access Restrictions are configured for the Function App to allow only requests from API Management:
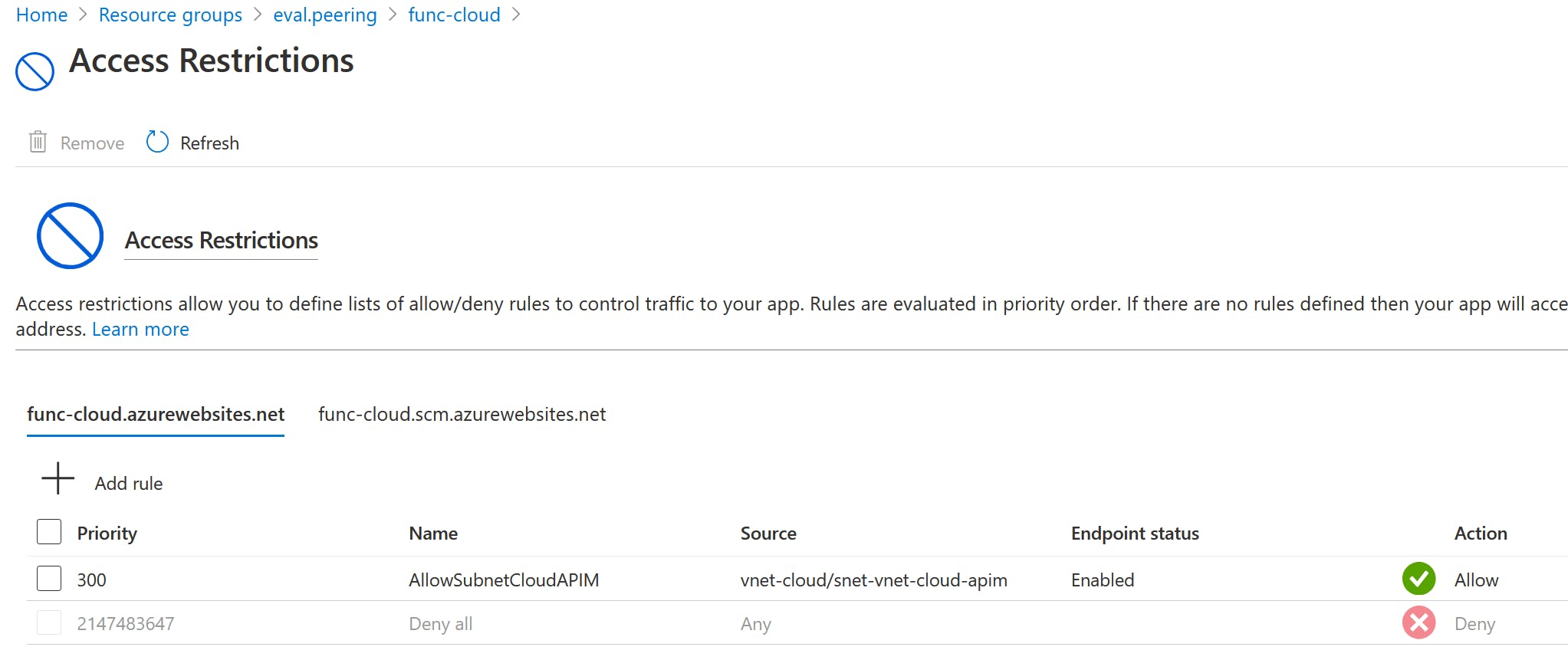
So, the Function App can only be accessed from Subnet snet-vnet-cloud-apim 172.16.252.0/22.
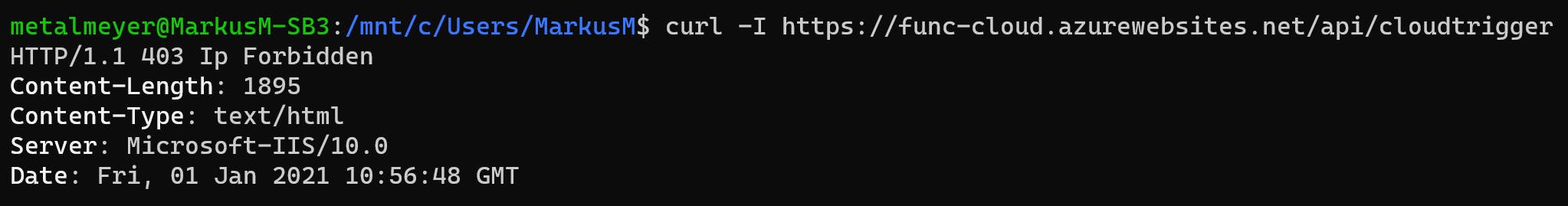
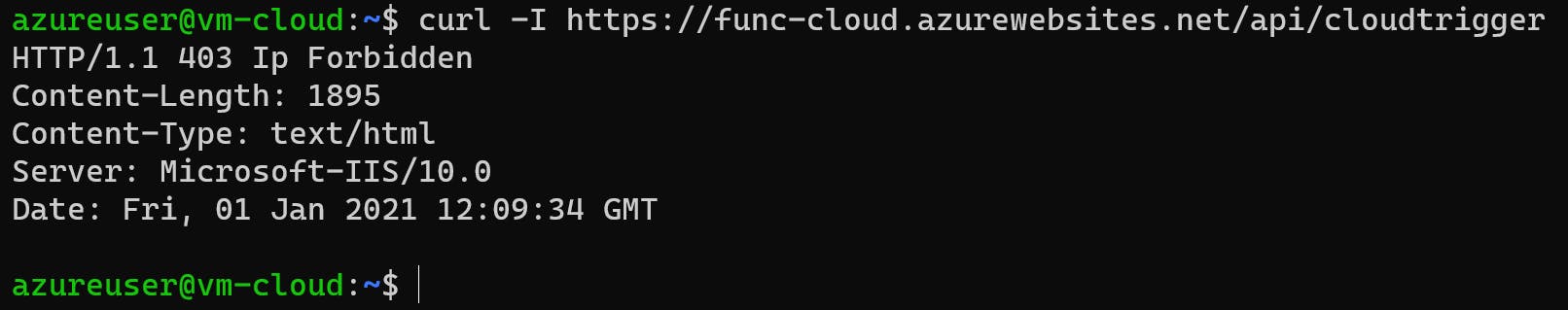
4.4 Lab API Management
API Management has one API with two operations which forwards the requests to the Azure Function Apps:
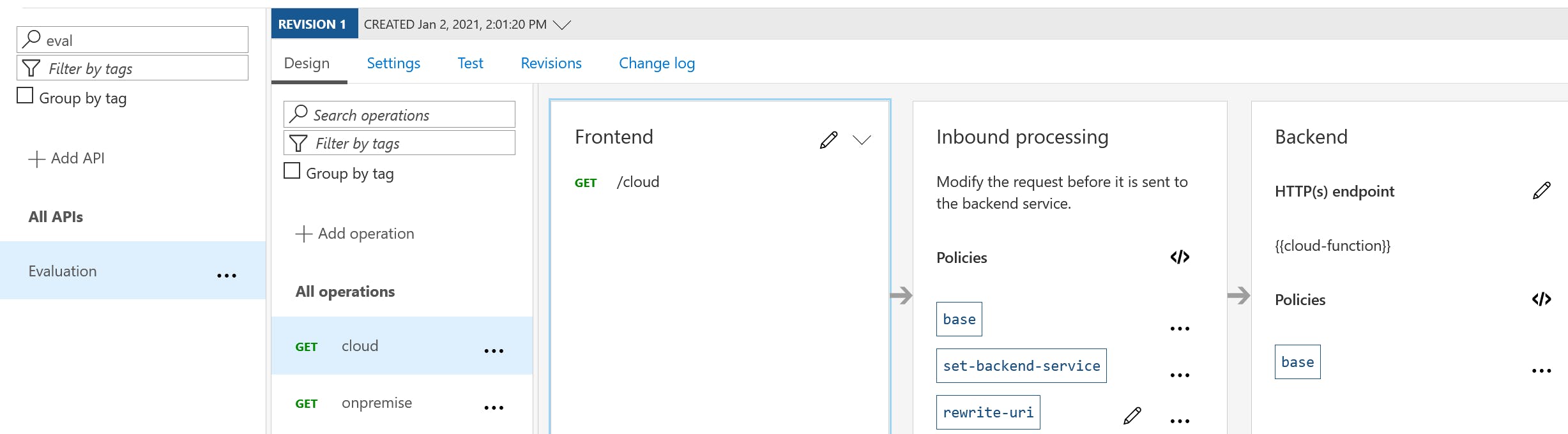
Policies:
/evaluation/cloud
cloud-function: func-cloud.azurewebsites.net/api
<inbound>
<base />
<set-backend-service base-url="{{cloud-function}}" />
<rewrite-uri template="/CloudTrigger" copy-unmatched-params="true" />
</inbound>
/evaluation/onpremise:
on-premise-function: func-on-premise.azurewebsites.net/api
<inbound>
<base />
<set-backend-service base-url="{{on-premise-function}}" />
<rewrite-uri template="/OnPremiseTrigger" copy-unmatched-params="true" />
</inbound>
4.4.1 Lab API Management - VNet
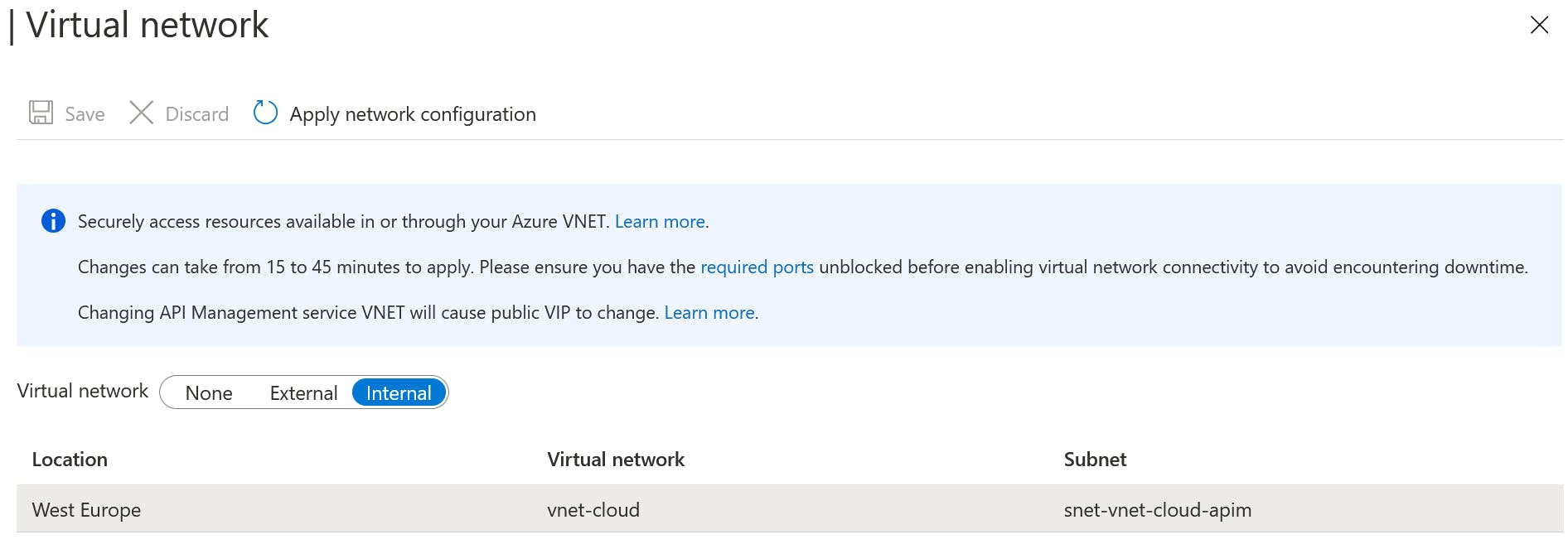
API Management is part of the VNet subnet snet-vnet-cloud-apim and deployed as an internal VNet.
4.5 Lab Data Flow and Requests
4.5.1 VM Cloud to On-Premise-Function
A request from the Cloud-VNet to API Management forwards the request to the Function in the On-Premise-VNet:
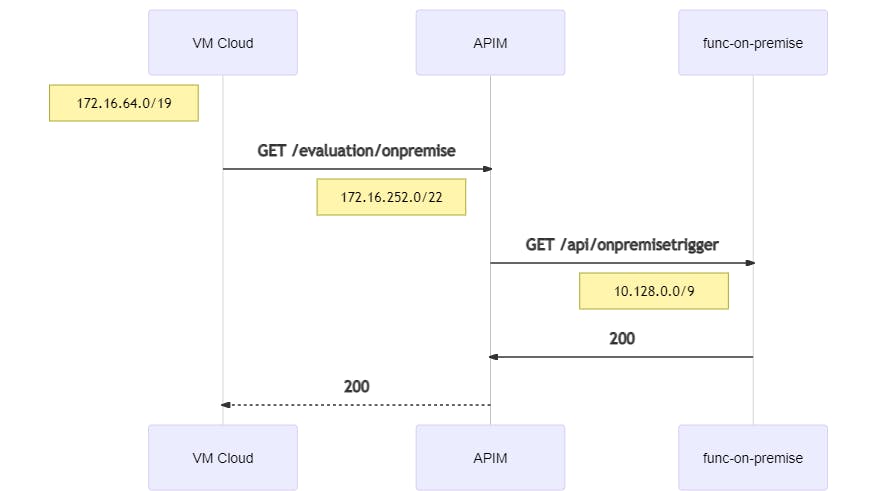
curl https://apim-eval-peering.azure-api.net/evaluation/onpremise

4.5.2 VM On-Premise to On-Premise-Function
A request from the On-Premise-VNet to API Management forwards the request to the Function in the On-Premise-VNet:
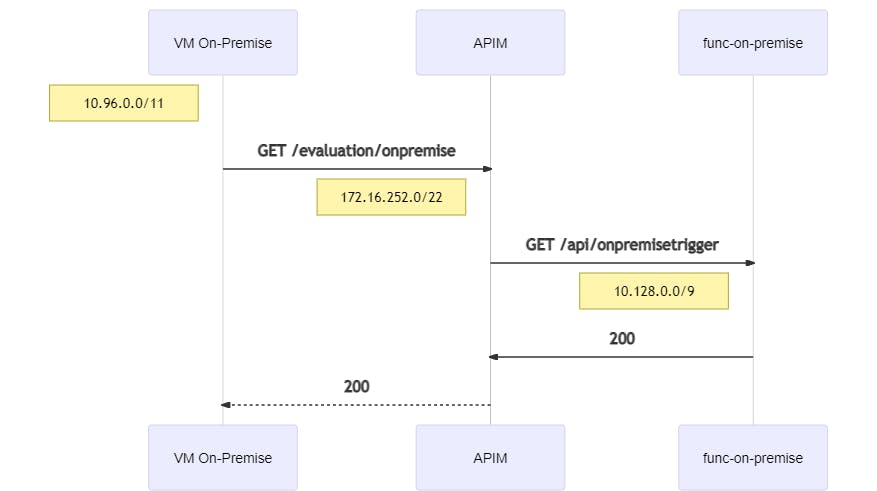
curl https://apim-eval-peering.azure-api.net/evaluation/onpremise

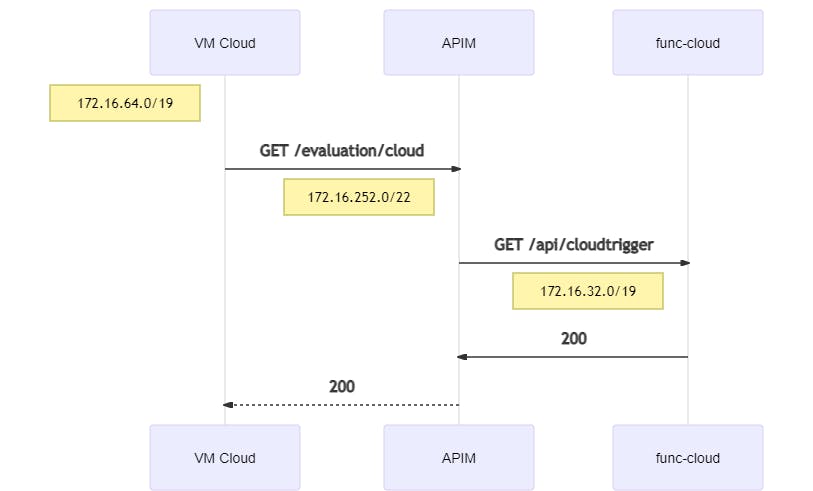
4.5.3 VM Cloud to Cloud-Function
A request from the Cloud-VNet to API Management forwards the request to the Function in the Cloud-VNet:
curl https://apim-eval-peering.azure-api.net/evaluation/cloud

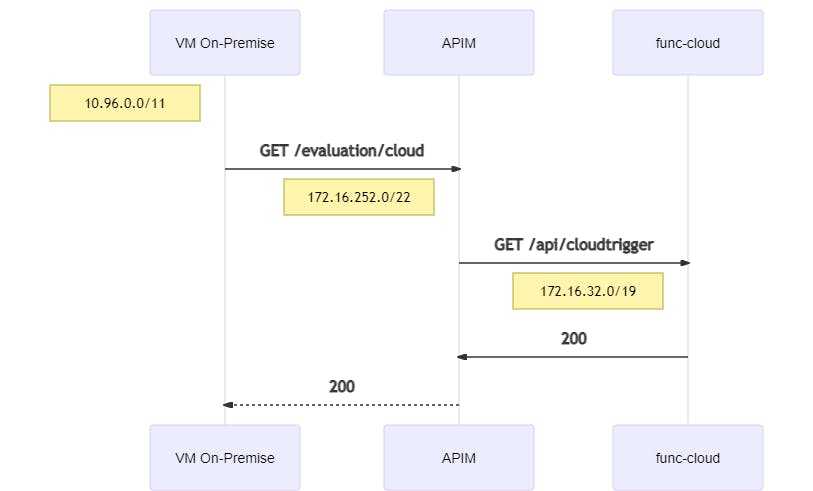
4.5.4 VM On-Premise to Cloud-Function
A request from the On-Premise-VNet to API Management forwards the request to the Function in the Cloud-VNet:
curl https://apim-eval-peering.azure-api.net/evaluation/cloud

5 Code and Deployment
The entire code can be found in GitHub.
All the resources (Azure resources, Function Apps, VMs) can be deployed with a script:
bash deploy.sh
Deploy only Azure resources:
6 Further information
Choosing between Azure VNet Peering and VNet Gateways
- VNet peering - connecting VNets within the same Azure region
- Global VNet peering - connecting VNets across Azure regions